Introduction
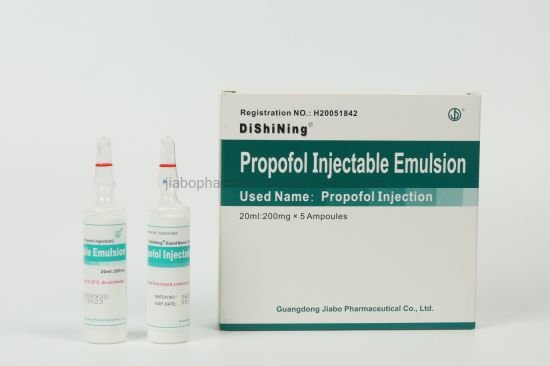
In the world of medicine, anesthetics play a crucial role in various procedures. It, also known as propofol, is a powerful short-acting intravenous anesthetic medication used to induce and maintain unconsciousness during surgery or other medical procedures. This article delves into the world of pofol, explaining its uses, benefits, potential side effects, and important considerations.
What is Pofol?
It is a milky white, odorless liquid medication administered through an intravenous (IV) line. It belongs to a class of drugs called general anesthetics. These medications work by affecting the central nervous system, causing temporary unconsciousness and preventing pain sensations.
Key terms:
- Intravenous (IV): Delivered through a vein.
- General anesthetic: Medication that induces unconsciousness and prevents pain.
- Central nervous system (CNS): The network of nerves and brain that controls body functions.
How Does Pofol Work?
The exact mechanism of how pofol works is still not fully understood. However, it’s believed to interact with various receptors in the brain, particularly those involved in regulating consciousness and pain perception. This interaction disrupts the normal signaling pathways, leading to a state of unconsciousness and pain relief.
Uses of Pofol
Pofol has a wide range of applications in various medical settings, including:
- Surgery: Used for inducing and maintaining anesthesia during surgeries of varying lengths and complexities.
- Medical procedures: Can be used for procedures that require pain relief and patient relaxation, such as endoscopies, colonoscopies, and bronchoscopies.
- Intensive care unit (ICU): May be used for sedation and pain management in critically ill patients who require mechanical ventilation.
Additional notes:
- Pofol is typically used in combination with other medications to manage pain, nausea, and vomiting during procedures.
- The dosage of pofol is carefully tailored based on individual factors like age, weight, and overall health.
Benefits
Pofol offers several advantages compared to other anesthetics:
- Rapid onset and offset: Takes effect quickly after administration and allows for rapid recovery after the procedure.
- Minimal nausea and vomiting: Less likely to cause nausea and vomiting compared to some other anesthetics.
- Versatility: Can be used for procedures of varying durations and complexities.
- Amnesia: Patients typically have no memory of the period during which they were under the effect of pofol.
Understanding the benefits helps healthcare professionals choose the most suitable anesthetic for each patient’s needs.
Potential Side Effects of Pofol
Like any medication, pofol can cause some side effects. These are usually mild and temporary but can sometimes be more serious. Here’s a breakdown of some common side effects:
- Pain at the injection site: May cause a burning sensation or discomfort at the IV insertion site.
- Low blood pressure: Can cause a temporary decrease in blood pressure.
- Respiratory depression: May slow down breathing, requiring temporary support with a ventilator.
- Allergic reactions: Rarely, it can cause allergic reactions, including skin rash, itching, and wheezing.
Serious side effects:
- Seizures: In rare cases, it can trigger seizures, especially in individuals with a history of seizure disorders.
- Myoclonus: Involuntary muscle jerks can occur during the administration of pofol.
- Cardiac arrhythmias: May cause irregular heartbeats in some patients.
It’s important to note that this is not an exhaustive list, and you should always discuss any potential risks and side effects with your doctor before receiving it.
Important Considerations with Pofol
Here are some crucial points to consider before receiving it:
- Medical history: Inform your doctor about any pre-existing medical conditions, allergies, or medications you are currently taking. This helps them assess potential interactions and adjust the medication accordingly.
- Pregnancy and breastfeeding: it can be used during pregnancy, but only when the potential benefits outweigh the risks. Discuss this thoroughly with your doctor if you are pregnant or breastfeeding.
- Alcohol and drug use: Disclose any recent alcohol or drug use to your doctor, as these substances can interact with pofol and affect its effectiveness.
Following your doctor’s instructions before, during, and after receiving it is essential for a safe and successful experience.
FAQs
Here are some frequently asked questions about this:
Is it painful?
The IV insertion itself might cause mild discomfort, but pofol itself doesn’t cause pain once it takes effect.
Is it addictive?
It is not typically considered addictive when used in a controlled medical setting. However, misuse outside of a medical environment can lead to dependence.
What happens when I wake up after use it?
Most people experience a smooth recovery after pofol. You might feel groggy or disoriented for a short while, but these effects should wear off quickly. Your doctor will monitor your recovery and provide instructions to ensure a safe and comfortable awakening.
Conclusion
Pofol is a powerful and versatile anesthetic medication used in various medical procedures. It offers rapid onset and offset, minimal nausea and vomiting, and amnesia for the procedure itself. However, like any medication, it can cause side effects. It’s crucial to discuss your medical history, allergies, and medications with your doctor before receiving it. Understanding the benefits, potential side effects, and important considerations will help you make informed decisions about your anesthesia care.



















Leave a Reply